
One sentence summary
This study introduces an ultra-sensitive method called CAPP-Seq for detecting and quantifying circulating tumor DNA, demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity in non-small cell lung cancer, offering new possibilities for early cancer detection and personalized treatment.
Background
The background of this study is rooted in the potential of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as a non-invasive biomarker for assessing tumor burden. However, existing methods for ctDNA detection and quantification have been limited in their sensitivity and patient coverage for broad clinical application. The researchers observed that ctDNA could be detected in the majority of patients with various types of cancers, and its levels correlated with tumor volume. These observations led to the development of CAPP-Seq, a cost-effective and ultra-sensitive method for quantifying ctDNA, aiming to enhance the clinical utility of ctDNA in cancer detection and monitoring.
Method
- The study utilized a method known as CAPP-Seq (CAncer Personalized Profiling by deep Sequencing) for the detection and quantification of ctDNA in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
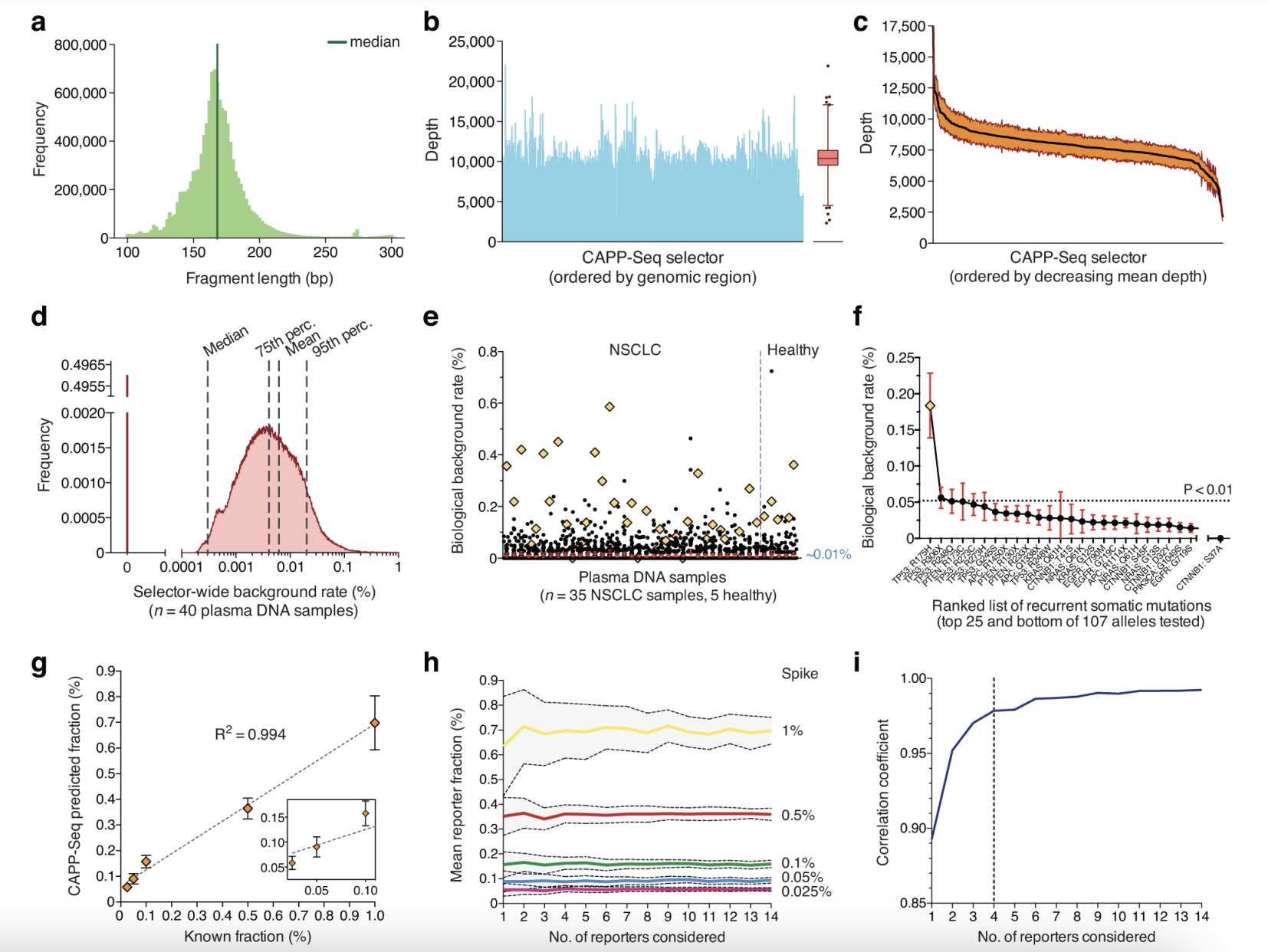
- The researchers designed a selector for CAPP-Seq that covers somatic mutations across various categories, enabling the identification of mutations in over 95% of tumors.
- The study implemented CAPP-Seq in NSCLC, conducting deep sequencing with an average coverage of approximately 10,000x, and analyzed a total of 90 samples, including two NSCLC cell lines, 17 primary tumor samples, and matched peripheral blood leukocytes, as well as 40 plasma samples from 18 individuals.
- The researchers used a decision tree to integrate the information content of multiple instances and categories of somatic mutations into a ctDNA detection index, which was then applied for disease monitoring and minimal residual disease detection.
Discussion
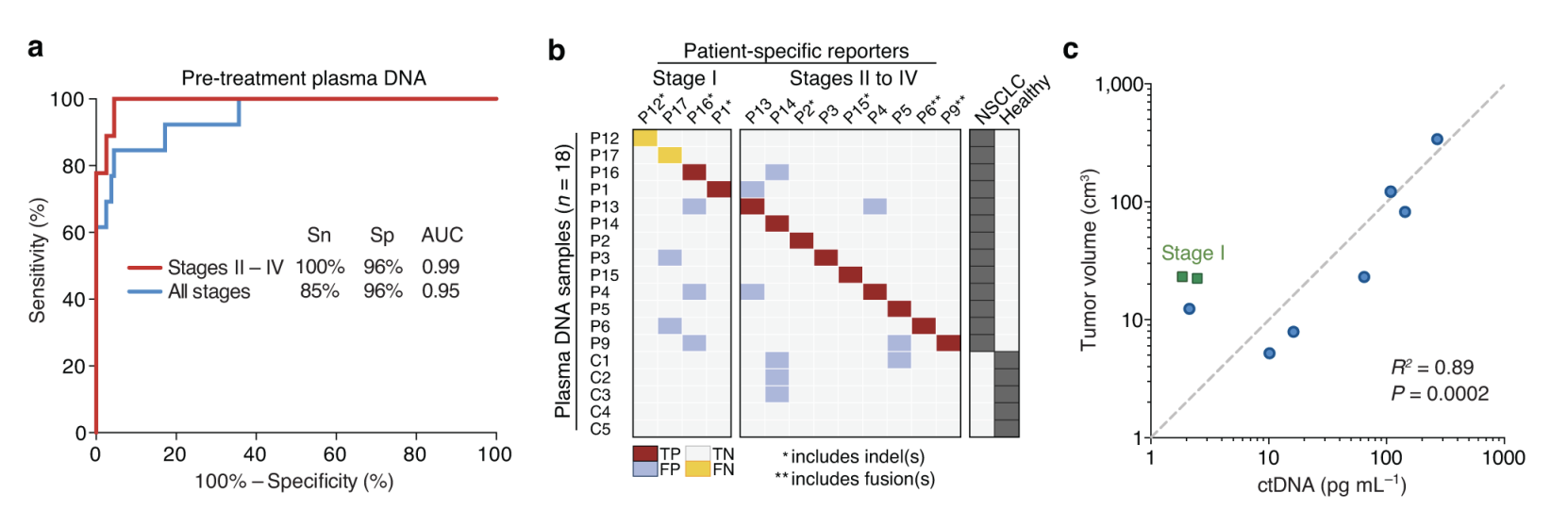
- The study found that the CAPP-Seq method could detect ctDNA in 100% of stage II-IV and 50% of stage I NSCLC patients, demonstrating a high sensitivity and specificity, and suggesting its potential for early cancer detection and monitoring.
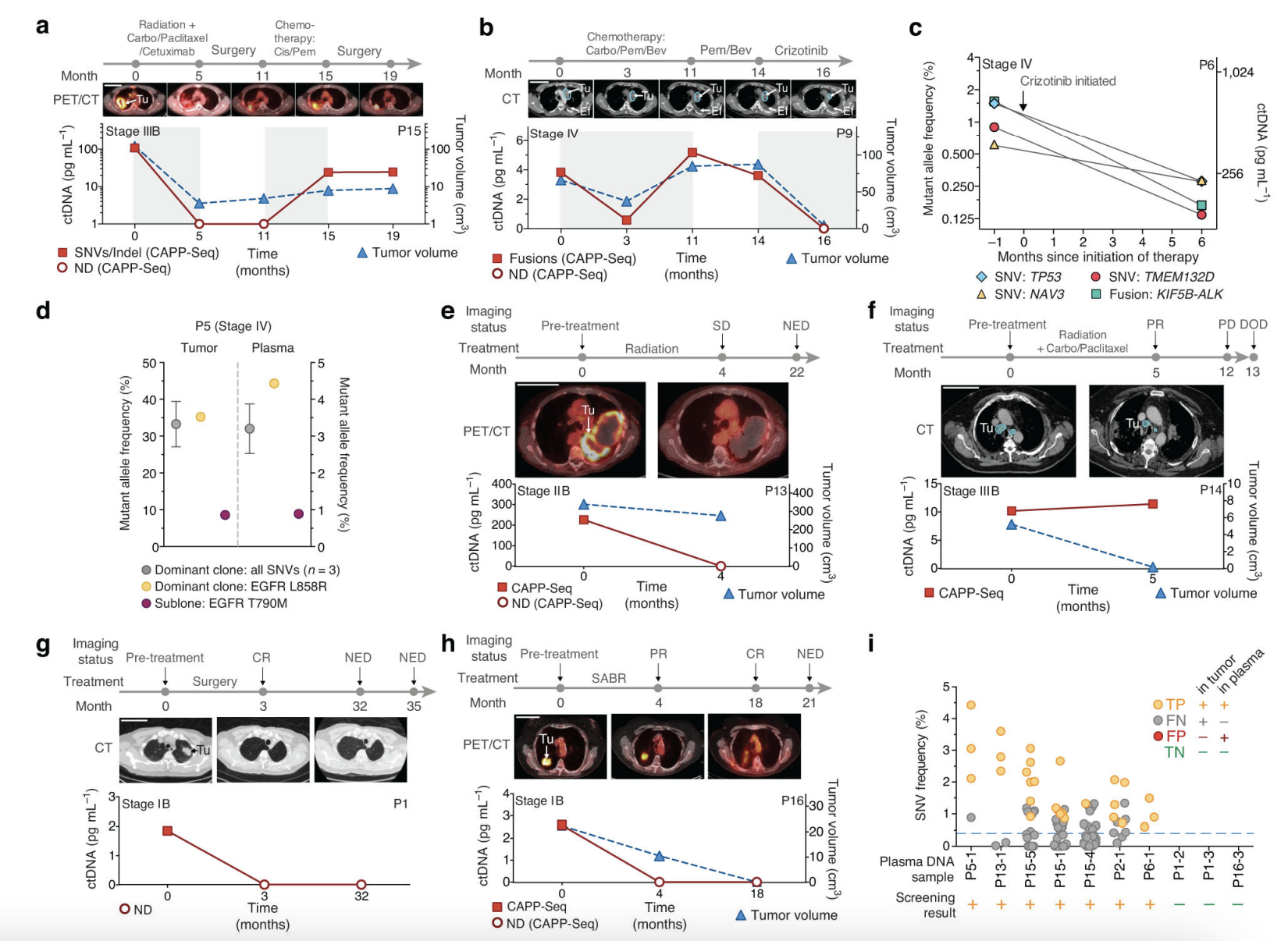
- The researchers observed a significant correlation between ctDNA levels and tumor volume, indicating that ctDNA could serve as a reliable biomarker for assessing tumor burden.
- The study also highlighted the potential of CAPP-Seq for distinguishing residual disease and treatment-related imaging changes, providing an earlier response assessment than radiographic methods.
- The researchers concluded that CAPP-Seq could be routinely applied in the clinic for the detection and monitoring of various malignancies, thereby promoting personalized cancer treatment.
Reading summary
What is the motivation?
The study was inspired by the limitations of existing methods for detecting and quantifying ctDNA, a promising non-invasive biomarker for assessing tumor burden. The researchers aimed to address these limitations by developing a more sensitive and broadly applicable method, with the potential to significantly enhance the clinical utility of ctDNA in cancer management.
What is the novelty & contribution?
The study introduces CAPP-Seq, an innovative and ultra-sensitive method for ctDNA detection and quantification. This method, tested in NSCLC, demonstrated superior sensitivity and specificity compared to previous approaches. Furthermore, the researchers established a strong correlation between ctDNA levels and tumor volume, reinforcing the credibility of ctDNA as a biomarker. This work paves the way for improved early cancer detection and monitoring, potentially advancing personalized cancer treatment strategies.